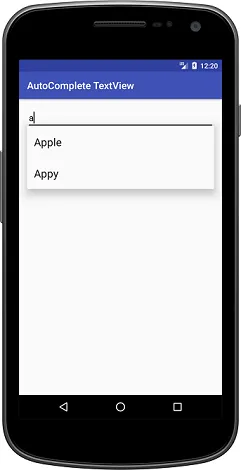
AutocompleteTextView is like a changeable text field, which intelligently suggests words as we type. This list of options appears in a dropdown that we can select to replace the words in the text box.
We can close the dropdown at any time by pressing the back key or, if we have nothing selected in the dropdown, we can close it by pressing the enter key or the middle dpad button.
This list of suggestions is taken from the data adapter and only appears after we type a certain number of characters, which is determined by a limit.
You can display and close the Autocomplete dropdown in the following way:
yourAutoComplete.showDropDown() yourAutoComplete.dismissDropDown()
Here is a code example that shows how to create an AutoCompleteTextView that suggests fruit names as we type:
First, implement the AutocompleteTextView component in your xml view, then enable it with the following coding.
// Import library for AutoCompleteTextView import android.widget.ArrayAdapter; import android.widget.AutoCompleteTextView; // Get a reference to the AutoCompleteTextView in the XML layout AutoCompleteTextView autoCompleteTextView = findViewById(R.id.autoCompleteTextView); // Create a list containing the names of fruits String[] listFruits = { "Apple" , "Orange" , "Mango" , "Grape" , "Banana" , "Strawberry" }; // Create an adapter for AutoCompleteTextView ArrayAdapter<String> adapter = new ArrayAdapter<>( this , android.R.layout.simple_dropdown_item_1line, daftarBuah); // Set the adapter to AutoCompleteTextView autoCompleteTextView.setAdapter(adapter); // Set the character limit for displaying suggestions autoCompleteTextView.setThreshold( 1 );
Example of Custom Autocomplete TextView
Create data model Fruit.java (Model class/POJO)
public class Fruit { private int image; private String name; private String desc; public int getImage () { return image; } public void setImage ( int image) { this .image = image; } public String getName () { return name; } public void setName (String name) { this .name = name; } public String getDesc () { return desc; } public void setDesc (String desc) { this .desc = desc; } }
<?xml version= ” 1.0 " encoding=”utf-8" ?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android= ” http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android " android:layout_width= ” match_parent ” android:layout_height= ” wrap_content ” android:orientation= ” horizontal ” android:padding= ” 8d p ” > <ImageView android:id= ”@ +id/imageView ” android:layout_width= ” wrap_content ” android:layout_height= ” wrap_content ” /> <TextView android:id= ”@ +id/textView ” android:layout_width= ” wrap_content ” android:layout_height= ” wrap_content ” android:padding= ” 4d p ” android:textColor= ” # 000000 " android:textSize= ” 18 sp ” / > </LinearLayout>
import android.app.Activity; import android.content.Context; import android.support.annotation.NonNull; import android.support.annotation.Nullable; import android.util.Log; import android.view.LayoutInflater; import android.view.View; import android.view.ViewGroup; import android.widget.ArrayAdapter; import android.widget.Filter; import android.widget.ImageView; import android.widget.TextView; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class FruitAdapter extends ArrayAdapter<Fruit> { private Context context; private int resourceId; private List<Fruit> items, tempItems, suggestions; public FruitAdapter (@NonNull Context context, int resourceId, ArrayList<Fruit> items) { super(context, resourceId, items); this .items = items; this .context = context; this .resourceId = resourceId; tempItems = new ArrayList<>(items); suggestions = new ArrayList<>(); } @NonNull @Override public View getView ( int position, @Nullable View convertView, @NonNull ViewGroup parent) { View view = convertView; try { if (convertView == null ) { LayoutInflater inflater = ((Activity) context).getLayoutInflater(); view = inflater.inflate(resourceId, parent, false ); } Fruit fruit = getItem(position); TextView name = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.textView); ImageView imageView = view.findViewById(R.id.imageView); imageView.setImageResource(fruit.getImage()); name.setText(fruit.getName()); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return view; } @Nullable @Override public Fruit getItem ( int position) { return items. get (position); } @Override public int getCount () { return items.size(); } @Override public long getItemId ( int position) { return position; } @NonNull @Override public Filter getFilter () { return fruitFilter; } private Filter fruitFilter = new Filter() { @Override public CharSequence convertResultToString (Object resultValue) { Fruit fruit = (Fruit) resultValue; return fruit.getName(); } @Override protected FilterResults performFiltering (CharSequence charSequence) { if (charSequence != null ) { suggestions.clear(); for (Fruit fruit: tempItems) { if (fruit.getName().toLowerCase().startsWith(charSequence.toString().toLowerCase())) { suggestions.add(fruit); } } FilterResults filterResults = new FilterResults(); filterResults.values = suggestions; filterResults.count = suggestions.size(); return filterResults; } else { return new FilterResults (); } } @Override protected void publishResults (CharSequence charSequence, FilterResults filterResults) { ArrayList<Fruit> tempValues = (ArrayList<Fruit>) filterResults.values; if (filterResults != null && filterResults.count > 0 ) { clear(); for (Fruit fruitObj : tempValues) { add(fruitObj); } notifyDataSetChanged(); } else { clear(); notifyDataSetChanged(); } } }; }
package com.example.demoproject ; import android.os.Bundle; import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.support.v7.widget.AppCompatAutoCompleteTextView; import android.view.View; import android.widget.AdapterView; import android.widget.ArrayAdapter; import android.widget.TextView; import java.util.ArrayList; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private ArrayList<Fruit> fruitArrayList; private AppCompatAutoCompleteTextView autoTextViewCustom; private TextView fruitDesc; private FruitAdapter fruitAdapter; @Override protected void onCreate (Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); fruitDesc = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.fruitDesc); autoTextViewCustom = (AppCompatAutoCompleteTextView) findViewById(R.id.autoTextViewCustom); // fill fruit list fruitArrayList = new ArrayList<>(); fruitArrayList.add( new Fruit(R.drawable.apple, “ Apple ” , “ The apple tree is a deciduous tree in the rose family best known for its sweet, pomaceous fruit, the apple. ” )); fruitArrayList.add( new Fruit(R.drawable.banana, “ Banana ” , “ The banana is an edible fruit — botanically a berry — produced by several kinds of large herbaceous flowering plants in the genus Musa. ” )); fruitArrayList.add( new Fruit(R.drawable.cherries, “ Cherry ” , “ A cherry is the fruit of many plants of the genus Prunus, and is a fleshy drupe (stone fruit). ” )); fruitArrayList.add( new Fruit(R.drawable.grapes, “ Grape ” , “ A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus Vitis. ” )); fruitArrayList.add( new Fruit(R.drawable.kiwi, “ Kiwi ” , “ Kiwifruit or Chinese gooseberry is the edible berries of several species of woody vines in the genus Actinidia. ” )); fruitArrayList.add( new Fruit(R.drawable.mango, “ Mango ” , “ Mangoes are juicy stone fruit from numerous species of tropical trees belonging to the flowering plant genus Mangifera, cultivated mostly for their edible fruit. ” )); fruitArrayList.add( new Fruit(R.drawable.pear, “ Pear ” , “ The pear is any of several tree and shrub species of the genus Pyrus, in the family Rosaceae. ” )); fruitAdapter = new FruitAdapter( this , R.layout.custom_row, fruitArrayList); autoTextViewCustom.setThreshold( 1 ); autoTextViewCustom.setAdapter(fruitAdapter); // handle click event and set desc on textview autoTextViewCustom.setOnItemClickListener( new AdapterView.OnItemClickListener() { @Override public void onItemClick (AdapterView<?> adapterView, View view, int i, long l) { Fruit fruit = (Fruit) adapterView.getItemAtPosition(i); fruitDesc.setText(fruit.getDesc()); } }); } }